SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTION[II] [3 Marks] – Year 2007
1. (a) What is ‘environmental pollution’?
(b) Distinguish between biodegradable and non-biodegradable pollutants.
(c) Choose the biodegradable pollutants from the list given below:
Sewage, DDT, radioactive waste, agricultural waste. [Delhi]
Answer. (a) Environmental pollution is an undesirable change in the physical, chemical or biological
characteristics of the natural environment, brought about by man’s activities. This pollution may affect the soil, rivers, seas or the atmosphere.

(c) Biodegradable pollutants are sewage and agricultural waste.
(b) Distinguish between biodegradable and non-biodegradable pollutants.
(c) Choose the biodegradable pollutants from the list given below:
Sewage, DDT, radioactive waste, agricultural waste. [Delhi]
Answer. (a) Environmental pollution is an undesirable change in the physical, chemical or biological
characteristics of the natural environment, brought about by man’s activities. This pollution may affect the soil, rivers, seas or the atmosphere.

(c) Biodegradable pollutants are sewage and agricultural waste.
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS [1 Mark] – Year 2008
2. How is the increase in demand for energy affecting our environment adversely?
Answer. The increase in demand for energy affects our environment adversely. Due to this increase, pollutants like CO,C02 , S02, etc., are released in to the atmosphere which leads to greenhouse effect.
Answer. The increase in demand for energy affects our environment adversely. Due to this increase, pollutants like CO,C02 , S02, etc., are released in to the atmosphere which leads to greenhouse effect.
3. Why is ozone layer getting depleted at the higher levels of the atmosphere? [Delhi (C)]
Answer. Ozone layer is getting depleted at the higher levels of the atmosphere due to effect of chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) which are used as refrigerants and in fire extinguishers.
Answer. Ozone layer is getting depleted at the higher levels of the atmosphere due to effect of chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) which are used as refrigerants and in fire extinguishers.
4. Name any two abiotic components of an environment. [Delhi (C)]
Answer. Two abiotic components of an environment are temperature and rainfall.
Answer. Two abiotic components of an environment are temperature and rainfall.
SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTION[II] [3 Marks] – Year 2008
5. Why are bacteria and fungi called decomposers? List any two advantages of decomposers to the environment. [Delhi]
Answer. Bacteria and fungi breakdown the dead remains and waste products of organisms. These micro organisms are called the decomposers as they breakdown the complex organic substances into simple inorganic substances that go into the soil and are used up once more by the plants.
Two advantages of decomposers to the environment are as follows:
Answer. Bacteria and fungi breakdown the dead remains and waste products of organisms. These micro organisms are called the decomposers as they breakdown the complex organic substances into simple inorganic substances that go into the soil and are used up once more by the plants.
Two advantages of decomposers to the environment are as follows:
- Decomposers feed, on the dead bodies of plants and animals. They return the simple components to soil and help in making the steady state of ecosystem by recycling of nutrients. They, therefore, create a balance in the environment.
- They also act as scavengers or cleansing agents of the atmosphere.
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS [1 Mark] – Year 2009
6. What are the two main components of our environment? [Delhi]
Answer. The two main components of our environment are the biotic or living components and abiotic or non-living components.
Answer. The two main components of our environment are the biotic or living components and abiotic or non-living components.
7. Why are green plants called ‘producers’? [All India]
Answer. Green plants are called ‘producers’ because they can produce food by photosynthesis in the presence of sunlight.
Answer. Green plants are called ‘producers’ because they can produce food by photosynthesis in the presence of sunlight.
8. Which disease is caused in human beings due to depletion of ozone layer in the atmosphere? [Foreign]
Answer. Skin cancer is caused in human beings due to the depletion of ozone layer in the atmosphere.
Answer. Skin cancer is caused in human beings due to the depletion of ozone layer in the atmosphere.
SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS [II] [2 Marks] – Year 2009
9. How is ozone formed in the upper atmosphere? Why is the damage of ozone layer a cause of concern to us? State a cause of this damage. [Delhi(C)]
Answer. Ozone is formed in upper atmosphere by the reaction of ultraviolet (UV) radiations on oxygen (02) molecule.
The damage to ozone layer is a cause of concern to us as due to its damage, more ultraviolet rays reach the earth’s surface causing various health hazards.

A cause of this damage is the presence of large amount of chlorofluorocarbons in the atmosphere.
Answer. Ozone is formed in upper atmosphere by the reaction of ultraviolet (UV) radiations on oxygen (02) molecule.
The damage to ozone layer is a cause of concern to us as due to its damage, more ultraviolet rays reach the earth’s surface causing various health hazards.

A cause of this damage is the presence of large amount of chlorofluorocarbons in the atmosphere.
10. State two problems caused by the non- biodegradable waste that we generate in our daily life. [All India (C)]
Answer. Two problems caused by non-biodegradable waste that we generate in our daily life are:
Answer. Two problems caused by non-biodegradable waste that we generate in our daily life are:
- It clogs drains.
- It causes water and soil pollution.
11. What are biodegradable and non- biodegradable substances? Select two biodegradable pollutants from the following: Agricultural waste, glass, plastic, sewage, DDT. [Ail India (C)]
Answer. Biodegradable substances are those substances which are broken down into simpler, harmless substances in nature in due course of time by the biological processes such as micro organisms like certain bacteria.
Non-biodegradable substances are those substances which cannot be broken down into simpler, harmless substances in nature.
Two biodegradable pollutants are agricultural waste and sewage.
Answer. Biodegradable substances are those substances which are broken down into simpler, harmless substances in nature in due course of time by the biological processes such as micro organisms like certain bacteria.
Non-biodegradable substances are those substances which cannot be broken down into simpler, harmless substances in nature.
Two biodegradable pollutants are agricultural waste and sewage.
SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS [I] [2 Marks] – Year 2010
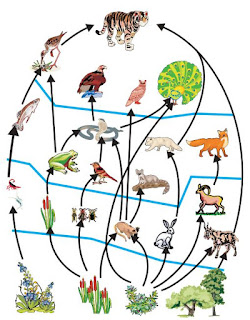
12. Construct an aquatic food chain showing four trophic levels. [All India]
Answer. Food chain in aquatic ecosystem:

Answer. Food chain in aquatic ecosystem:
13. Explain ‘biological magnification’ with the help of an example. [All India]
Answer. Pesticides used in crops are washed down .into the soil. From soil these are absorbed by plants along with water and minerals and thus, they enter the food chain. While consuming the crops, human beings also consume these pesticides which get accumulated in our bodies. This phenomenon is known as biological magnification.
Answer. Pesticides used in crops are washed down .into the soil. From soil these are absorbed by plants along with water and minerals and thus, they enter the food chain. While consuming the crops, human beings also consume these pesticides which get accumulated in our bodies. This phenomenon is known as biological magnification.
14. Describe how decomposers facilitate recycling of matter in order to maintain balance in the ecosystem. [Foreign]
Answer. Decomposers are micro organisms that obtain energy from the chemical breakdown of dead organisms of animals or plants. These micro organisms breakdown the complex organic substances of dead organisms into simple inorganic substances that go into the soil and are used up once more by the plants. Decomposers thus, help in recycling of matter.
Answer. Decomposers are micro organisms that obtain energy from the chemical breakdown of dead organisms of animals or plants. These micro organisms breakdown the complex organic substances of dead organisms into simple inorganic substances that go into the soil and are used up once more by the plants. Decomposers thus, help in recycling of matter.
15. Explain the phenomenon of “biological magnification” How does it affect organisms belonging to different trophic levels particularly the tertiary consumers? [Delhi]
Answer. The process in which harmful chemicals enter a food chain and get accumulated progressively at each trophic level is called biological magnification.
Harmful and toxic chemicals enter our bodies when they are added to soil and water. Use of pesticides to protect the food crops from diseases and pests and chemical wastes of factories are dumped in open or disposed off into rivers. These chemicals are washed down into the soil and ultimately to water table or get absorbed or taken up from the soil by the plants along with water and minerals and in this way harmful chemicals enter the food chain. The quantity of these harmful chemicals increase with increase in trophic level of the food chain because these substances are not degradable. Man is at the top of the food chain, so concentration is maximum in human beings.
Thus, accumulation of DDT has been maximum in man as DDT is used to destroy pests. DDT is accumulated in the following way in this food chain:
This is the reason why our food grains such as wheat and rice, vegetables and fruits and even meat contain varying amounts of pesticides residues. So, the highest trophic level at the extreme right of food chain has the maximum concentration of harmful chemicals in a food chain.

Answer. The process in which harmful chemicals enter a food chain and get accumulated progressively at each trophic level is called biological magnification.
Harmful and toxic chemicals enter our bodies when they are added to soil and water. Use of pesticides to protect the food crops from diseases and pests and chemical wastes of factories are dumped in open or disposed off into rivers. These chemicals are washed down into the soil and ultimately to water table or get absorbed or taken up from the soil by the plants along with water and minerals and in this way harmful chemicals enter the food chain. The quantity of these harmful chemicals increase with increase in trophic level of the food chain because these substances are not degradable. Man is at the top of the food chain, so concentration is maximum in human beings.
Thus, accumulation of DDT has been maximum in man as DDT is used to destroy pests. DDT is accumulated in the following way in this food chain:
This is the reason why our food grains such as wheat and rice, vegetables and fruits and even meat contain varying amounts of pesticides residues. So, the highest trophic level at the extreme right of food chain has the maximum concentration of harmful chemicals in a food chain.

16. “Damage to the ozone layer is a cause for concern.” Justify this statement. Suggest any two steps to limit this damage. ‘ [Delhi]
Answer. Ozone layer prevents the harmful ultraviolet radiation to enter the atmosphere and reach the earth’s surface. Depletion of ozone layer has become a cause for concern because it can cause serious effects on human body and other organisms of the environment like fatal diseases such as skin cancer, changes in genetic material DNA, eye damage, etc.
Two steps to limit this damage are as follows:
Answer. Ozone layer prevents the harmful ultraviolet radiation to enter the atmosphere and reach the earth’s surface. Depletion of ozone layer has become a cause for concern because it can cause serious effects on human body and other organisms of the environment like fatal diseases such as skin cancer, changes in genetic material DNA, eye damage, etc.
Two steps to limit this damage are as follows:
- Judicious use of aerosol spray propellants such as fluorocarbon and chlorofluorocarbons which cause depletion or hole in ozone layer.
- Control over large scale nuclear explosions and limited use of supersonic planes.
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS [1 Mark] – Year 2011
17. What will happen if we kill all the organisms in one trophic level? [Delhi]
Answer. If we kill all the organisms in one trophic level, the following effects will take place:
Answer. If we kill all the organisms in one trophic level, the following effects will take place:
- The population of organisms in previous trophi’c level will increase.
- The organisms in next trophic level will not be able to get the food, so they will migrate to some other ecosystem or die.
- It will cause an ecological imbalance in the food chain.
18. Why did United Nations act to control the production of chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) used in refrigerators? [Delhi]
Answer. CFCs deplete the ozone layer around the earth, hence their production is controlled by United Nations.
Answer. CFCs deplete the ozone layer around the earth, hence their production is controlled by United Nations.
19. Which compounds are responsible for the depletion of ozone layer? [Delhi]
Answer. The compounds responsible for the depletion of ozone layer are chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs).
Answer. The compounds responsible for the depletion of ozone layer are chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs).
20. Define ‘trophic level’. [Delhi]
Answer. Trophic level is the position that an organism occupies in a food chain, where transfer of food or energy takes place.
Answer. Trophic level is the position that an organism occupies in a food chain, where transfer of food or energy takes place.
21. What are the various steps in a food chain called? [Delhi]
Answer. The various steps in a food chain are called trophic levels.
Answer. The various steps in a food chain are called trophic levels.
22. What is the important function of presence of ozone in earth’s atmosphere? [Delhi]
Answer. The important function of presence of ozone in earth’s atmosphere is that it shields the surface of the earth from ultraviolet (UV) radiations of the sun.
Answer. The important function of presence of ozone in earth’s atmosphere is that it shields the surface of the earth from ultraviolet (UV) radiations of the sun.
23. Give an example to illustrate that indiscriminate use of pesticides may result-in the degradation of the environment. [All India]
Answer. The pesticides used in crop field are washed down into the water bodies. From water bodies, these are absorbed by aquatic plants and animals of a food chain and thereby degrades the environment.
Answer. The pesticides used in crop field are washed down into the water bodies. From water bodies, these are absorbed by aquatic plants and animals of a food chain and thereby degrades the environment.
24. Why is it necessary to conserve our environment? [All India]
Answer. It is necessary to conserve our environment to prevent depletion of natural resources and environmental damage, thereby sustaining life.
Answer. It is necessary to conserve our environment to prevent depletion of natural resources and environmental damage, thereby sustaining life.
25. What is meant by a biodegradable waste? [All India]
Answer. Biodegradable wastes are those substances which are broken down into simpler, harmless substances in nature in due course of time by the biological processes such as action of micro organisms like certain bacteria.
Examples: Urine and faecal matter, sewage, agricultural residue, paper, wood, cloth and cattle dung.
Answer. Biodegradable wastes are those substances which are broken down into simpler, harmless substances in nature in due course of time by the biological processes such as action of micro organisms like certain bacteria.
Examples: Urine and faecal matter, sewage, agricultural residue, paper, wood, cloth and cattle dung.
26. What is the role of decomposers in the ecosystem? [Foreign]
Answer. Role of decomposers in the environment:
Answer. Role of decomposers in the environment:
- They return the nutrients to the nutrient pool.
- They help in completing the different bio-geochemical cycles, thus they maintain the balance in the ecosystem.
27. What step is being taken to limit the damage to the ozone layer? [Foreign]
Answer.
Answer.
- Judicious use of aerosol spray propellants such as fluorocarbon and chlorofluorocarbons which cause depletion or hole in ozone layer.
- Control over large scale nuclear explosions and limited use of supersonic planes.
28. Why are some substances non- biodegradable? [Foreign]
Answer. Some substances are non-biodegradable because they cannot be broken down into simpler harmless substances in nature.
Answer. Some substances are non-biodegradable because they cannot be broken down into simpler harmless substances in nature.
29. Which class of chemicals is linked to the decrease in the amount of ozone in the upper atmosphere of the earth? [Delhi]
Answer. The chemical compound Chlorofluorocarbon is responsible for decrease of ozone in the upper atmosphere of the earth.
Answer. The chemical compound Chlorofluorocarbon is responsible for decrease of ozone in the upper atmosphere of the earth.
30. Name two decomposers operating in our ecosystem. [All India 2011; Delhi]
Answer. Bacteria and fungi.
Answer. Bacteria and fungi.
31. Select two non-biodegradable substances from the following waste generated in a kitchen: spoilt food, paper bags, milk bags, vegetable peels, tin cans, used tea leaves. [Delhi]
Answer. Milk bags and tin cans.
Answer. Milk bags and tin cans.
32. What happens when higher energy ultraviolet radiations act on the oxygen at the higher level of the atmosphere? [All India]
Answer. When high energy ultraviolet radiations act on oxygen, ozone is produced:

Answer. When high energy ultraviolet radiations act on oxygen, ozone is produced:

33. In a food chain, 10,000 joules of energy is available to the producer. How much energy will be available to the secondary consumer to transfer it to the tertiary consumer? [All India ]
Answer. 10 J will be available to the secondary consumer to transfer to the tertiary consumer.
Answer. 10 J will be available to the secondary consumer to transfer to the tertiary consumer.
34. Write the name and formula of a molecule made up of three atoms of oxygen. [All India]
Answer. Ozone and its chemical formula is O3.
Answer. Ozone and its chemical formula is O3.
35. List two man-made ecosystems. [All India]
Answer. Garden and Pond are man-made ecosystems.
Answer. Garden and Pond are man-made ecosystems.
36. Consider the following food chain which occurs in a forest: Grass -> Deer -> Lion
If 10000 J of solar energy is available to the grass, how much energy would be available to the deer to transfer it to the lion? [Foreign]
Answer. 10 J energy would be available to deer to transfer to lion.
If 10000 J of solar energy is available to the grass, how much energy would be available to the deer to transfer it to the lion? [Foreign]
Answer. 10 J energy would be available to deer to transfer to lion.
37. Which of the following belong to the first trophic level of a food chain? Grass, Grasshopper, Plants, Rat, Tiger [Foreign]
Answer. Grass and plants belong to the 1st trophic level of a food chain.
Answer. Grass and plants belong to the 1st trophic level of a food chain.
38. Name the phenomenon in which non-biodegradable chemicals get accumulated progressively at each trophic level of a food chain. [Foreign]
Answer. Biological magnification.
Other Important Questions
Answer. Biological magnification.
Other Important Questions
1.Why is there a need to b an the use of poly then e bags?
Ans.Polythene bags are non- biodegradable, the y are not decomposed by micro- organisms hence, cause land pollution.
2.What are the two functions of ecosystem?
Ans.Interactions of any ecosystem refers to it s functions these interactions are-
(A) Biogeochemical cycles- The cyclic transfers between the living and non- living components.
(B) Flow of energy- in a food chain, through various st eps of eating and being eaten food energy flow from one tropic level t o another.
3.What percentage of solar energy is trapped and utilized by plants?
Ans.Plants utilized only 1% of total sun’s ener gy, which is utilized by plants in the process of photosynthesis.
4.Energy transfer is said to be unidirectional wh e r e as biochemical transfer is said be cyclic. Why?
Ans.Energy flow is unidirectional because as it transfers from one trophic level to next trophic level, it reduces only 10% is available at Successive level from previous level. Nutrient flow is cyclic because nutrients re turned back into nutrient pool from the dead bodies of plants and animals by the d ecomposition of micro- organisms from nutrient pool. They are utilized aga in by plants.
5.Give difference between produc es and consumers.
Ans.
6.There are no predators for tiger or lion. Why?
Ans. Lions and tigers are at the highest trophic level. They are largest animals which feed upon the secondary carnivores like wolves etc. they are not killed and eaten by other animals.
7.What are the measures to protect ozone depletion?
Ans..Measure to protect ozone layer-
(A) Concern over increasing global ozone depletion led to international restrictions in the use and manufacture of CFCS and halons.
(B) International concern over the seriousness of the problems associated with ozone layer depletion led to the adoption of Vienna convention for the protection of the ozone layers in 1985.
(C) Promotion of an international treaty know
Ans.Polythene bags are non- biodegradable, the y are not decomposed by micro- organisms hence, cause land pollution.
2.What are the two functions of ecosystem?
Ans.Interactions of any ecosystem refers to it s functions these interactions are-
(A) Biogeochemical cycles- The cyclic transfers between the living and non- living components.
(B) Flow of energy- in a food chain, through various st eps of eating and being eaten food energy flow from one tropic level t o another.
3.What percentage of solar energy is trapped and utilized by plants?
Ans.Plants utilized only 1% of total sun’s ener gy, which is utilized by plants in the process of photosynthesis.
4.Energy transfer is said to be unidirectional wh e r e as biochemical transfer is said be cyclic. Why?
Ans.Energy flow is unidirectional because as it transfers from one trophic level to next trophic level, it reduces only 10% is available at Successive level from previous level. Nutrient flow is cyclic because nutrients re turned back into nutrient pool from the dead bodies of plants and animals by the d ecomposition of micro- organisms from nutrient pool. They are utilized aga in by plants.
5.Give difference between produc es and consumers.
Ans.
6.There are no predators for tiger or lion. Why?
Ans. Lions and tigers are at the highest trophic level. They are largest animals which feed upon the secondary carnivores like wolves etc. they are not killed and eaten by other animals.
7.What are the measures to protect ozone depletion?
Ans..Measure to protect ozone layer-
(A) Concern over increasing global ozone depletion led to international restrictions in the use and manufacture of CFCS and halons.
(B) International concern over the seriousness of the problems associated with ozone layer depletion led to the adoption of Vienna convention for the protection of the ozone layers in 1985.
(C) Promotion of an international treaty know